
# cat /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600īasically it means do not install nsight-compute and nsight-systems from "**" and put a high priority for packages with "l=NVIDIA CUDA".ĥ.2 Download and install CUDA repository meta-data wget The content of APT preferences fragment file is: Sudo mv cuda-ubuntu1804.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600 Here I decided to choose CUDA 11.0.3 for Ubuntu 18.04 using Debian installer method, so using below link to download:Ĭhoose "Linux"->"X86_64"->"Ubuntu"->"18.04"->"deb(local)".ĥ.1 Download the APT preferences fragment file which controls which versions of packages will be selected for installation. Sudo apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r) Then install linux-headers package for that kernel version: Verify the System has the Correct Kernel Headers and Development Packages Installed Note: gcc is required for development using CUDA Toolkit, not required for running CUDA applications.Ĥ. Native Linux Distribution Support in CUDA 11.2" in CUDA Installation guide. Note: Please refer to OS support matrix "Table 1. Verify OS version uname -m & cat /etc/*release Note: update-pciids fetches the current version of the pci.ids file from the primary distribution site and installs it.Ģ. Subsystem: NVIDIA Corporation Quadro RTX 6000 # update-pciidsĭownloaded daily snapshot dated 03:15:02ġ7:00.0 VGA compatible controller : NVIDIA Corporation TU102GL (rev a1) (prog-if 00 ) It is my recommendation to reboot after performing the kernel-headers upgrade/install process, and after installing CUDA – to verify that everything is loaded correctly.This article records each step for installing CUDA Toolkit and NVIDIA Driver on Ubuntu by following CUDA installation guide.ġ. | N/A 54C P0 68W / 235W | 0MiB / 11439MiB | 0% Default |Īfter installing a new version of CUDA, there are some situations that require rebooting the machine to have the driver versions load properly. | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr.

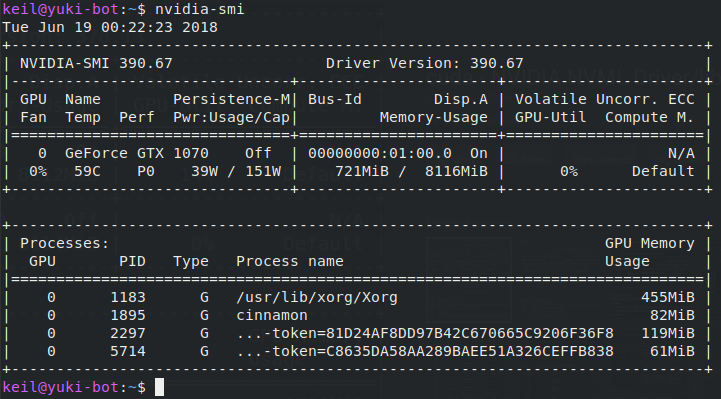
The driver version is 367.48 as seen below, and the cards are two Tesla K40m. In many cases, I just use nvidia-smi to check the CUDA version on CentOS and Ubuntu.įor me, nvidia-smi is the most straight-forward and simplest way to get a holistic view of everything – both GPU card model and driver version, as well as some additional information like the topology of the cards on the PCIe bus, temperatures, memory utilization, and more. Identifying which GPU card is installed and what version NVRM version: NVIDIA UNIX x86_64 Kernel Module 367.48 Sat Sep 3 18:21: You can also use the kernel to run a CUDA version check: ~ $ cat /proc/driver/nvidia/version } Identifying which CUDA driver version is installed and active in the kernel Int driver_version = 0, runtime_version = 0 You can find a full example of using cudaDriverGetVersion() here: #include The API call gets the CUDA version from the active driver, currently loaded in Linux or Windows. When you’re writing your own code, figuring out how to check the CUDA version, including capabilities is often accomplished with the cudaDriverGetVersion () API call. Figure out which one is the relevant one for you, and modify the environment variables to match, or get rid of the older versions. Note that if the nvcc version doesn’t match the driver version, you may have multiple nvccs in your PATH. This means that we have CUDA version 8.0.61 installed. You can check nvcc -version to get the CUDA compiler version, which matches the toolkit version: ~ $ nvcc -versionĬopyright (c) 2005-2016 NVIDIA CorporationĬuda compilation tools, release 8.0, V8.0.61 If you have installed the CUDA toolkit but which nvcc returns no results, you might need to add the directory to your path. If that appears, your NVCC is installed in the standard directory. You should see something like /usr/bin/nvcc. Run which nvcc to find if nvcc is installed properly. Check if CUDA is installed and it’s location with NVCC There are several ways and steps you could check which CUDA version is installed on your Linux box.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
